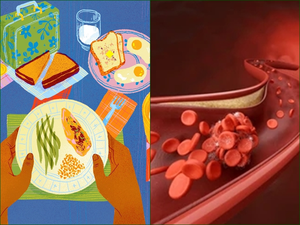
New York, Feb 20 (IANS) While eating protein is essential for good health, US researchers have discovered a molecular mechanism by which excessive dietary protein could increase atherosclerosis risk.
Atherosclerosis is the build-up of fats, cholesterol and other substances in and on the artery walls.
The study, which combined small human trials with experiments in mice and cells in a Petri dish, showed that consuming over 22 per cent of dietary calories from protein can lead to increased activation of immune cells that play a role in atherosclerotic plaque formation, driving the disease risk.
Furthermore, the scientists showed that one amino acid — leucine — seems to have a disproportionate role in driving the pathological pathways linked to atherosclerosis, or stiff, hardened arteries.
“Our study shows that dialing up your protein intake in pursuit of better metabolic health is not a panacea. You could be doing real damage to your arteries,” said Babak Razani, Professor of cardiology at University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine.
“Our hope is that this research starts a conversation about ways of modifying diets in a precise manner that can influence body function at a molecular level and dampen disease risks,” Razani added.
The findings are published in the journal Nature Metabolism.
Previous studies have also shown that overreliance on protein may not be such a good thing for long-term health.
Following their 2020 research, in which Razani’s laboratory first showed that excess dietary protein increases atherosclerosis risk in mice, his next study in collaboration with Bettina Mittendorfer, a metabolism expert at the University of Missouri, Columbia, delved deeper into the potential mechanism and its relevance to the human body.
“We have shown in our mechanistic studies that amino acids, which are really the building blocks of the protein, can trigger disease through specific signaling mechanisms and then also alter the metabolism of these cells,” Mittendorfer said.
“For instance, small immune cells in the vasculature called macrophages can trigger the development of atherosclerosis.”
Based on initial experiments in healthy human subjects to determine the timeline of immune cell activation following ingestion of protein-enriched meals, the researchers simulated similar conditions in mice and in human macrophages, immune cells that are shown to be particularly sensitive to amino acids derived from protein.
Their work showed that consuming more than 22 per cent of daily dietary calories through protein can negatively affect macrophages that are responsible for clearing out cellular debris, leading to the accumulation of a “graveyard” of those cells inside the vessel walls and worsening of atherosclerotic plaques overtime.
Interestingly, the analysis of circulating amino acids showed that leucine — an amino acid enriched in animal-derived foods like beef, eggs and milk — is primarily responsible for abnormal macrophage activation and atherosclerosis risk, suggesting a potential avenue for further research on personalised diet modification, or “precision nutrition.”
The findings are particularly relevant in hospital settings, where nutritionists often recommend protein-rich foods for the sickest patients to preserve muscle mass and strength.
“Perhaps blindly increasing protein load is wrong,” Razani said. “Instead, it’s important to look at the diet as a whole and suggest balanced meals that won’t inadvertently exacerbate cardiovascular conditions, especially in people at risk of heart disease and vessel disorders.”
Razani also notes that these findings suggest differences in leucine levels between diets enriched in plant and animal protein might explain the differences in their effect on cardiovascular and metabolic health.
“The potential for this type of mechanistic research to inform future dietary guidelines is quite exciting,” he said.
–IANS
rvt/svn
Disclaimer
The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. The information is provided by TodayIndia.news and while we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this website.
Through this website you are able to link to other websites which are not under the control of TodayIndia.news We have no control over the nature, content and availability of those sites. The inclusion of any links does not necessarily imply a recommendation or endorse the views expressed within them.
Every effort is made to keep the website up and running smoothly. However, TodayIndia.news takes no responsibility for, and will not be liable for, the website being temporarily unavailable due to technical issues beyond our control.
For any legal details or query please visit original source link given with news or click on Go to Source.
Our translation service aims to offer the most accurate translation possible and we rarely experience any issues with news post. However, as the translation is carried out by third part tool there is a possibility for error to cause the occasional inaccuracy. We therefore require you to accept this disclaimer before confirming any translation news with us.
If you are not willing to accept this disclaimer then we recommend reading news post in its original language.